Semi-supervised learning : Major varieties of learning problem

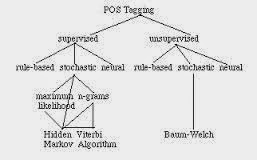
There are five types of learning problem that have received the preponderance of attention in machine learning. The first four are all cases of function estimation, grouped along two dimensions: whether the learning task is supervised or unsupervised, and whether the variable to be predicted is nominal or real-valued. Classification involves supervised learning of a function f (x) whose value is nominal, that is, drawn from a finite set of possible values. The learned function is called a classifier. It is given instances x of one or another class, and it must determine which class each instance belongs to; the value f (x) is the classifier’s prediction regarding the class of the instance. For example, an instance might be a particular word in context, and the classification task is to determine its part of speech. The learner is given labeled data consisting of a collection of instances along with the correct answer, that is, the correct class label, for each instance. The unsupervise...